Managing diabetes is a daily responsibility that goes beyond taking medications. For millions of individuals living with diabetes, maintaining healthy blood sugar levels requires a combination of diet, exercise, monitoring, and mental wellness. While healthcare providers in clinics and hospitals play a crucial role, much of diabetes management happens at home. This is where the guidance of skilled nurses becomes invaluable. Through education, practical tips, and personalized support, nurses help individuals take control of their health and prevent long-term complications.
Understanding Diabetes and Blood Sugar
Diabetes is a condition where the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or cannot use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps move glucose, or sugar, from the bloodstream into the cells to provide energy. When insulin function is impaired, blood sugar levels rise, leading to various health problems over time.
There are two primary types of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells, leading to little or no insulin production. Type 2 diabetes, more common in adults, occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough. Prediabetes is a warning stage, where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet in the diabetic range.
Blood sugar control is critical. Short-term spikes or dips can cause fatigue, dizziness, irritability, or confusion. Long-term uncontrolled diabetes increases the risk of serious complications, including neuropathy (nerve damage), kidney disease, heart problems, and vision loss. Home management of diabetes can be challenging, requiring careful monitoring of glucose, consistent meals, physical activity, and adherence to medication. Skilled nurses are trained to provide guidance, education, and support to help individuals manage these challenges effectively.
The Role of Skilled Nurses in Diabetes Care

Skilled nurses play a pivotal role in diabetes management, especially in the home setting. Their involvement goes beyond clinical care; they educate, empower, and support patients to make sustainable lifestyle changes.
Patient Education and Empowerment
Nurses teach patients how to monitor blood sugar levels, recognize symptoms of low or high glucose, and administer insulin or other medications correctly. Education also covers understanding food choices, portion sizes, and the impact of exercise on blood sugar. By providing clear instructions and practical demonstrations, nurses ensure that patients feel confident managing their condition.
Personalized Care Plans
Every individual’s diabetes journey is unique. Nurses assess lifestyle factors, comorbid conditions, and personal preferences to develop personalized care plans. This approach ensures recommendations are realistic and achievable, increasing the likelihood of adherence and long-term success.
Ongoing Support
Managing diabetes can be overwhelming, and setbacks are common. Skilled nurses offer ongoing support through regular check-ins, troubleshooting daily challenges, and motivating patients to stay consistent. Their encouragement and guidance can prevent discouragement and promote a sense of control over the condition.
Nutrition Guidance from Skilled Nurses

Diet is a cornerstone of diabetes management. The foods we eat directly affect blood sugar levels, making nutrition education a critical part of nurse-guided care.
Importance of Diet in Blood Sugar Control
A balanced diet helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. Meals should include a combination of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and fiber. Fiber, found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, slows the absorption of sugar, preventing rapid spikes. Proteins and healthy fats provide sustained energy and help regulate appetite.
Practical Tips from Nurses
Skilled nurses provide practical, everyday tips for managing diet at home:
- Meal prepping: Planning and preparing meals in advance reduces the temptation of high-sugar convenience foods.
- Reading nutrition labels: Nurses teach patients how to identify hidden sugars, sodium, and unhealthy fats.
- Healthy snacking: Suggestions include nuts, seeds, Greek yogurt, or fresh fruit to manage hunger between meals.
Special Considerations
Diet recommendations can vary based on age, activity level, and other health conditions. Nurses provide tailored guidance for seniors, children, or individuals with hypertension, kidney disease, or other comorbidities. Personalized meal plans make it easier to adhere to dietary recommendations without feeling deprived.
Exercise and Physical Activity

Physical activity is another critical component of diabetes management. Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, helps regulate blood sugar, supports weight management, and reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Why Movement Matters
Regular movement allows muscles to use glucose more efficiently, helping lower blood sugar levels. Exercise also supports cardiovascular health, reduces stress, and promotes overall well-being.
Safe Home Exercise Recommendations
For individuals managing diabetes at home, nurses recommend exercises that are safe and adaptable:
- Walking: A simple yet effective activity that can be done indoors or outdoors.
- Stretching and flexibility exercises: These improve circulation and reduce the risk of injuries.
- Resistance training: Using resistance bands or bodyweight exercises to build strength and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Chair exercises: Ideal for seniors or those with limited mobility.
How Nurses Guide Patients
Nurses work with patients to create realistic exercise routines based on mobility, fitness level, and health status. They also advise monitoring blood sugar before and after exercise to prevent hypoglycemia, particularly for individuals taking insulin or certain oral medications.
Medication Management at Home
Medication is often necessary to manage diabetes effectively, and proper administration is essential to avoid complications. Nurses provide guidance on the safe and effective use of medications, including oral medications and insulin.
Common Diabetes Medications
- Oral medications: These help improve insulin sensitivity, increase insulin production, or reduce glucose absorption.
- Insulin: Required for type 1 diabetes and sometimes for type 2, insulin helps regulate blood sugar levels when the body cannot produce enough.
The Nurse’s Role in Medication Adherence
Nurses ensure patients understand the correct dosing, timing, and storage of medications. They also demonstrate proper injection techniques, explain how to rotate injection sites, and monitor for side effects.
Safety Tips
- Avoid missing doses or double dosing.
- Be aware of interactions with other medications or supplements.
- Store insulin at recommended temperatures to maintain effectiveness.
- Keep a supply of quick-acting glucose for emergencies.
By providing structured guidance, nurses help prevent common medication-related mistakes and empower patients to take control of their treatment plan confidently.
Monitoring Blood Sugar and Health at Home

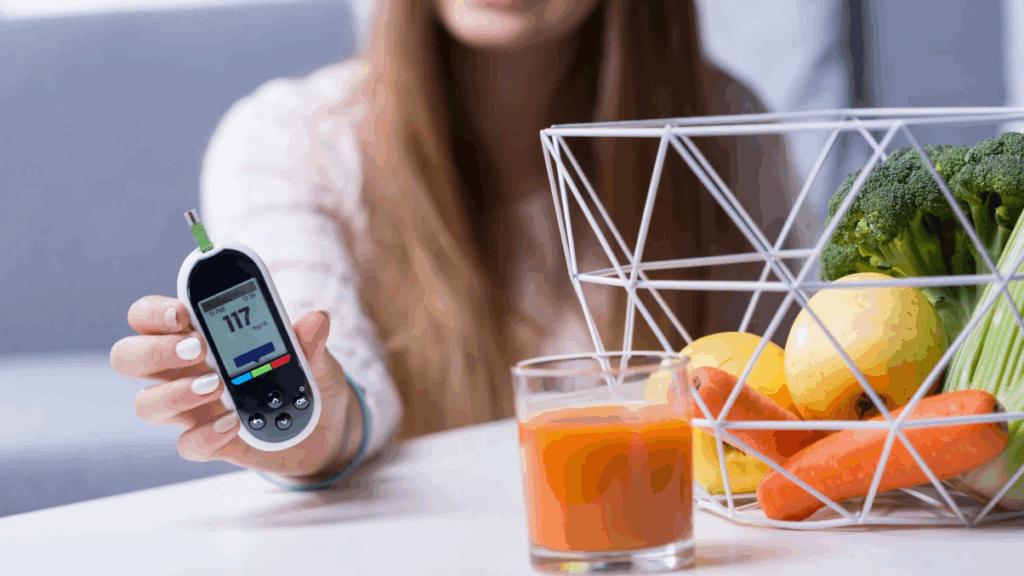
Monitoring blood glucose levels is essential for understanding patterns, preventing complications, and making informed lifestyle decisions.
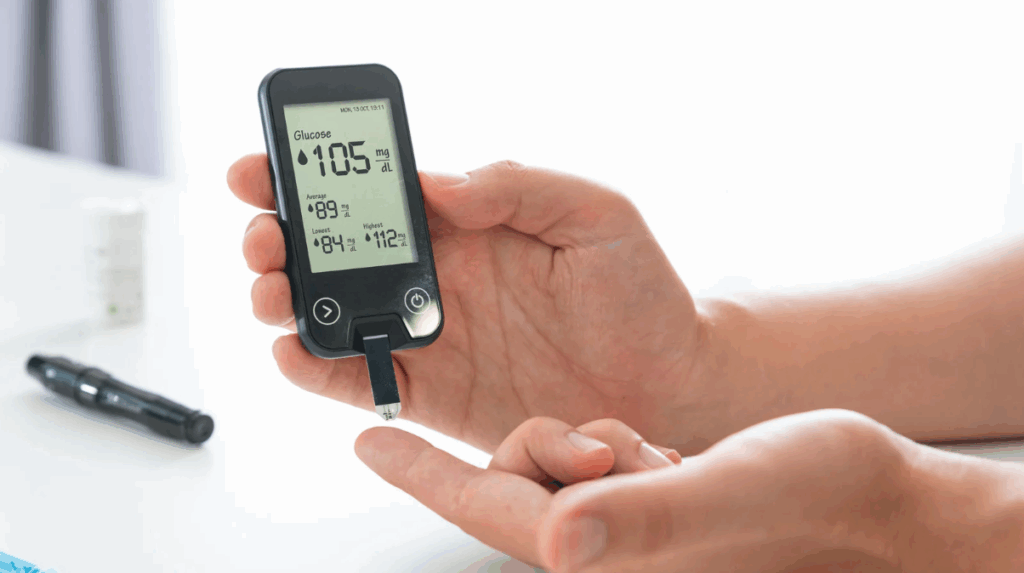
Blood Glucose Monitoring Basics
Patients can monitor blood sugar using fingerstick tests or continuous glucose monitors (CGMs). Nurses teach the proper techniques for accurate readings and explain target ranges. For most adults, fasting blood sugar should be between 80–130 mg/dL, and post-meal readings should be below 180 mg/dL, though individualized targets vary.
Tracking Patterns
Keeping a log of blood sugar readings, meals, physical activity, and medications helps identify trends. Skilled nurses can review these logs to adjust care plans, provide feedback, and anticipate potential problems before they become serious.
When to Seek Professional Help
Nurses educate patients on recognizing warning signs such as persistent high blood sugar, frequent hypoglycemia, unusual fatigue, or sudden changes in vision or weight. Knowing when to contact a healthcare professional or seek urgent care is crucial for preventing complications.
Mental Health and Lifestyle Considerations
Living with a chronic condition like diabetes can take a toll on mental and emotional well-being. Stress, anxiety, and burnout are common and can negatively affect blood sugar control.
The Emotional Impact of Diabetes
Managing diabetes requires constant vigilance, which can lead to frustration, guilt, or depression. Emotional stress itself can elevate blood sugar levels, creating a challenging cycle.
Nurse-Guided Coping Strategies
Skilled nurses help patients address mental health challenges through:
- Mindfulness and relaxation techniques: Deep breathing, meditation, and yoga.
- Support groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges provides motivation and emotional support.
- Realistic goal-setting: Encouraging achievable milestones and celebrating progress.
- Self-compassion: Helping patients avoid guilt for occasional setbacks and focus on long-term management.
By addressing mental health alongside physical health, nurses provide comprehensive guidance that improves overall well-being.
Creating a Diabetes-Friendly Home Environment

A supportive home environment can significantly improve diabetes management. Nurses guide patients on organizing their homes to promote healthier habits and reduce stress.
Organizing the Home for Success
- Food storage: Keep healthy snacks accessible and limit sugary or processed foods.
- Exercise-friendly spaces: Dedicate an area for stretching or resistance training to encourage consistent activity.
- Medical supplies: Store glucose monitors, testing strips, insulin, and medications in a convenient, organized manner.
Family Involvement
Family support is essential. Nurses encourage educating family members about diabetes, so they can provide encouragement, reminders, and assistance when needed.
Technology and Tools
Digital tools can support home diabetes management:
- Mobile apps for logging meals, blood sugar, and physical activity.
- CGMs that provide real-time blood sugar data and trend analysis.
- Smart pillboxes or reminders to improve medication adherence.
These tools, combined with nurse guidance, create an environment that promotes consistency and proactive health management.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes at home requires more than willpower—it requires knowledge, planning, and ongoing support. Skilled nurses from Genezen Home Health Care provide personalized education, practical guidance, and encouragement to help patients take control of their health. From nutrition and exercise to medication management, mental wellness, and home organization, our nurse-led lifestyle guidance empowers individuals to maintain healthier blood sugar levels, prevent complications, and enjoy a better quality of life.
By partnering with Genezen Home Health Care, patients gain more than instructions—they gain confidence, independence, and the tools needed for long-term success. Whether you are newly diagnosed or have been managing diabetes for years, our compassionate team is here to help you thrive at home, reach your health goals, and live each day with greater energy and peace of mind.
Take the first step today—contact us to schedule a consultation and learn how our skilled nurses can support your diabetes management at home.


